Izradu internetske stranice sufinancirala je Europska unija u okviru operativnog programa Konkurentnost i kohezija iz Europskog fonda za regionalni razvoj.
saznajte više
Plant description:
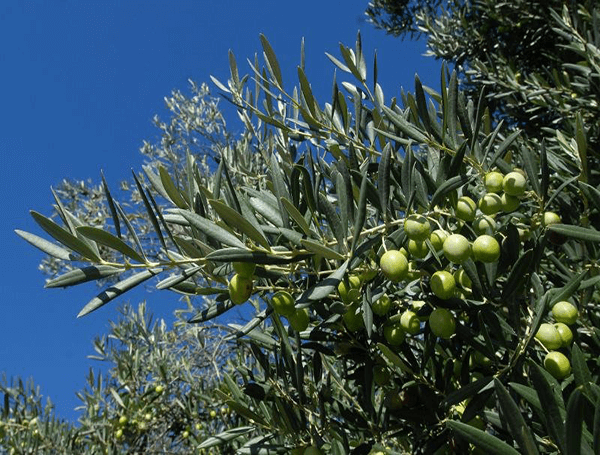
The olive tree, Olea europaea, is an evergreen tree or shrub native to the Mediterranean, Asia, and Africa. It is short and squat, and rarely exceeds 8–15 m (26–49 ft) in height. ‘Pisciottana’, a unique variety comprising 40,000 trees found only in the area around Pisciotta in the Campania region of southern Italy often exceeds this, with correspondingly large trunk diameters. The silvery green leaves are oblong, measuring 4–10 cm (1.6–3.9 in) long and 1–3 cm (0.39–1.18 in) wide. The trunk is typically gnarled and twisted. The small, white, feathery flowers, with ten-cleft calyx and corolla, two stamens, and bifid stigma, are borne generally on the previous year’s wood, in racemes springing from the axils of the leaves. The fruit is a small drupe 1–2.5 cm (0.39–0.98 in) long, thinner-fleshed and smaller in wild plants than in orchard cultivars. Olives are harvested in the green to purple stage. Olea europaea contains a seed commonly referred to in American English as a pit or a rock, and in British English as a stone.
Pharmaceutical use:
The oil is used in cosmetics, medicine, cooking, and soaps, and was also used as a fuel for traditional lamps. Olive oil originally came from the Mediterranean, but today it is used worldwide. Over the last 50 years, many studies have looked at the health benefits of olive oil.
Olive oil is the main source of dietary fat in the Mediterranean diet. There appears to be a lower death rate from cardiovascular diseases in the Mediterranean area, compared with other parts of the world. A review of studies carried out in Barcelona, Spain, looked at the biological and clinical effects of olive oil. Results suggested that people who regularly consume olive oil are less likely to develop cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension (high blood pressure), stroke, and hyperlipidemia (high blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels). Olive oil intake also appears to help reduce inflammation, endothelial dysfunction (problems with the inner linings of blood vessels), thrombosis, and carbohydrate metabolism. Use olive oil as a gentle moisturizer for dry skin.Olive oil has the same healthy fats as avocado, and plumps and moisturizes the skin with a combination of vitamin E and vitamin A.Dry, itchy and inflamed skin is usually the sign of skin irritations, such as eczema and psoriasis. Free radicals, sun and pollution can all take a toll on your skin. A study performed by dermatologist Leslie Baumann and published in a 2007 issue of “The Journal of Pathology” found that vitamin E was successful in fighting free radicals, photo aging and damage to maintain younger looking skin.
Cautions:
Please be aware that herbs, although natural can interact with certain medications, and that they may be ill advised to use under certain health conditions. Please consult a qualified health practitioner for cautions pertinent to you.
No therapeutic claim is made or intended for AZENA products. Information is for educational purposes only.