Izradu internetske stranice sufinancirala je Europska unija u okviru operativnog programa Konkurentnost i kohezija iz Europskog fonda za regionalni razvoj.
saznajte više
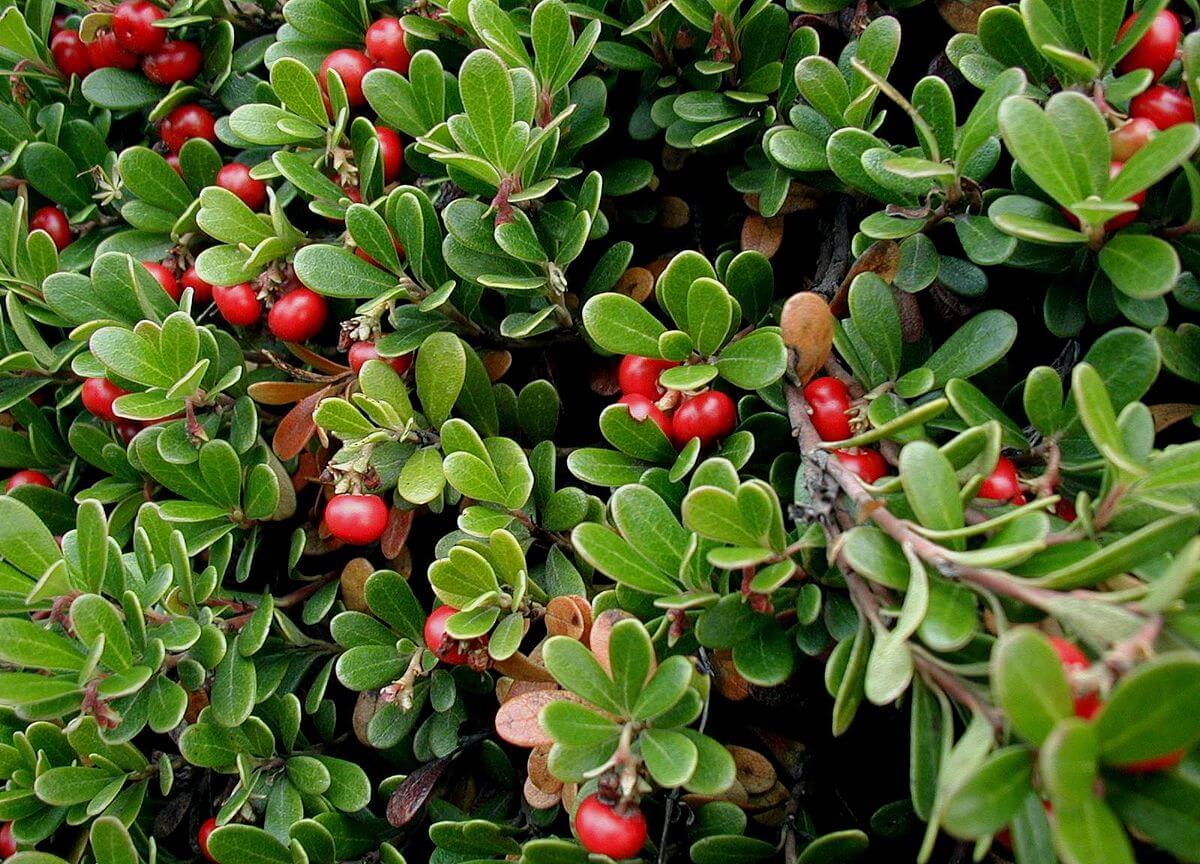

BEARBERRY
lat. Arctostaphylos uva ursi
Other names: Uva ursi, hogberry, manzanita, kinnikinnik, rockberry, beargrape.
Scroll
Habitat:
Bearberry is well suited to sub-Arctic zones, and may be found at those latitudes worldwide. It is particularly common in Central and Northern Europe, but may also be found growing in the wild in North America as well as isolated instances in more southerly regions at high elevations.
Description:
Uva ursi is any one of a variety of low-profile bushes that grow to the height of around 20 cm. The plant has a thick bark and leathery oval leaves that are about 1.5 cm in length. The bark is usually covered in fine, silky hairs. The flowers are either pink or white and have five distinct petals, each one less than a cm in length. It grows a red fruit that is often confused with a relative, the American cranberry.
Plant Parts Used:
Leaves and stems, flowers in season.
Pharmaceutical use:
Bearberry purportedly gets its name from the fact that the berries seem to be a favorite food of bears. Uva ursi acts as a natural diuretic. It has been used historically to treat cystitis, urolithiasis, and other urinary tract infections. It is a traditional bladder treatment used in European folk medicine. In northern Europe and Eurasia, bearberry tea has been a traditional herbal treatment for hundreds of years. Some Native American tribes used an infusion of the stems of bearberry and blueberry as a way to prevent miscarriage, and aid a woman’s recovery after childbirth. The leaves of uva ursi contain a very powerful and recognized antibacterial chemical compound known as hydroquinones. This is a scientifically proven compound, but its use is questioned by the US Food and Drug Administration, and the plant is not sanctioned for medical use in the United States. A tea made from a decoction of dried bearberry leaves is a traditional treatment for urinary tract infections in many parts of the world. Ingesting bearberry tea works best if the patient is on a vegetable-based diet. It has been clinically shown to be more effective when the urine is alkaline in nature. The folk remedies of many cultures suggest bearberry as an effective treatment for a backache, rheumatism, and arthritis. It is used as a disinfectant in some regions, perhaps due to its known attributes as a urinary antiseptic.
Cautions:
Please be aware that herbs, although natural can interact with certain medications, and that they may be ill advised to use under certain health conditions. Please consult a qualified health practitioner for cautions pertinent to you.
No therapeutic claim is made or intended for AZENA products. Information is for educational purposes only.